ReviewCoreASPHosting.NET | Best and cheap WordPress hosting. SEO is something many WordPress users talk about but never practice. This is because of the lingering myth that SEO is a complicated game. To win, it’s believed you need to have certain technical skills and deep knowledge of how search engines like Google work.
This simply isn’t true.
To get your WordPress content to rank higher in search, you don’t need to be an SEO expert. You just need to know – and practice – some simple writing, content structuring, and topic research skills. In this post, we’ll show you how to do this painlessly.
To start, let’s install a plugin that will serve as your guiding light for WordPress SEO.
Step 1: Install the Yoast SEO plugin
Yoast SEO is a WordPress plugin that helps you optimize posts and pages published on WordPress. It tells you exactly what to change in your content to make it search engine-friendly.
To install the Yoast SEO plugin:
- Click the Plugins option in the WP admin sidebar and select Add New
- In the search box, type “Yoast SEO” and hit Enter
- Click Install on the Yoast SEO box that appears
- After installation, activate the plugin
After Yoast is installed and activated, visit one of your WordPress posts and scroll to the bottom. You’ll see a Focus keyword and Analysis section. Enter the keyword you want to rank for with that post in the “Focus keyword” field and click Update or Save Changes on the right-hand side.
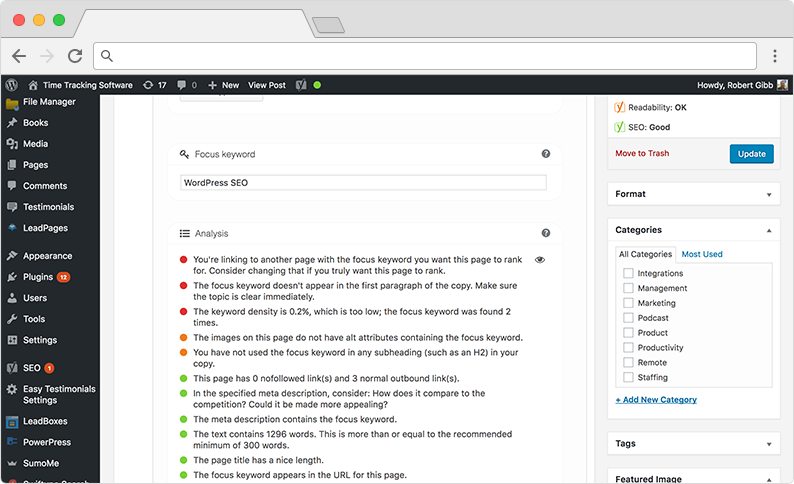
When the page refreshes, scroll to the bottom again to see a full analysis of your page. The screenshot above is an analysis of this post you’re currently reading about WordPress SEO.
Ideally you want all of the circles to be green. Follow the advice Yoast provides to make this happen. (The reason our circles aren’t all green is because we took this screenshot while writing and optimizing the post.)
Step 2: Fix permalinks and shorten URLs
The Permalink settings determine the URL structure of your posts and pages. How URLs are structured plays a role in how content ranks in search.
To configure permalinks, click Settings in the admin sidebar and select Permalinks. On the page, select the Post name option. Most SEO experts agree that the “Post name” permalink structure is best.
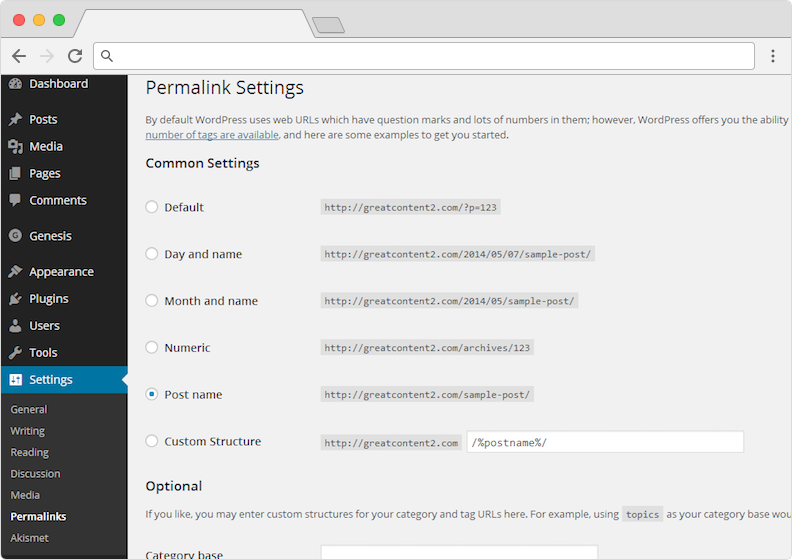
This does not necessarily mean you should keep the /%postname%/ structure when you publish. It’s just a good default to have. For good SEO, you should keep the permalink section of your posts to 2-4 letters. (For instance, for this post it’s /wordpress-seo/.)
Step 3: Give people what they’re looking for
What follows is good advice for anyone running a site – even if it’s not powered by WordPress. Consider this the “human aspect” of SEO. To maximize the effect of the tactics mentioned in Steps 1 and 2, it’s important to get these things right…
Understand search behavior
How would a potential customer search for a web design firm in York? How specific would the query be? Would your site be at the top of the list or on the third page? Any SEO strategy has to adapt to user searches, so devote part of your day to investigating them.
Use a reliable keyword suggestion tool to see which terms have a lot of traction and might give you an edge. Also, stay up to date on changes to Google’s search algorithm.
Address customer needs
People go to the web to look for things they need. It could be a product or tips on how to achieve a particular goal. When thinking about how to optimize your WordPress site, keep these needs in mind.
For instance, say you sell shoes in Topeka. People can get shoes anywhere, but most people are looking for something extra like low prices or a hot designer. Incorporate this extra something into your SEO efforts so people looking for “Steve Madden shoes Topeka” can find it on your site.
Step 4: SEO-friendly Themes and Plugins
WordPress comes with many features and is pre-configured for SEO right-out-of-the-box. The code is also relatively clean so it loads pretty fast. Page load time is increasingly becoming an important SEO factor. There isn’t been any direct evidence to show that sites that load faster enjoy better rankings, but the fact is, fast loading sites offer better user experience.
Anything that users love is good with Google.
This is why you must be careful choose the plugins you install to extend the functionality of your WordPress sites. While WordPress is great in its default state, some themes and plugins are bad for SEO. The following are some of issues you should consider before you install a theme or plugin.
Responsiveness
Everyone is going mobile. It is now an accepted fact that mobile page views will soon overtook desktop page views. You must therefore take this into account when installing a plugin or theme. Make sure it is responsive. Responsive web design takes into account optimal viewing experience across a range of devices. Users should be able to easily navigate your site on desktops, tablets and mobile phones without having to scroll, pan and resize. Read the documentation carefully and test out the site on a desktop computer and several mobile devices. Also, test the site on all major browsers to ensure that it is accessible from any browser.
Support for Schema Markup
Schema is one of the least utilized forms of SEO available. It isn’t utilized as much as it should be because many webmasters don’t understand how it works. Grasping the concept of schema and applying it on your WordPress website can give you a significant boost in search engine rankings. Schema markup is code put on websites to help search engines return more accurate results to users. Schema markup not only tells search engines what your data means, but what it says as well. A team from Google, Yahoo and Bing collaborated to create Schema.org, the site for Schema markup.
You don’t need to learn any new code. Sites with Schema still use HTML but you also add Schema vocabulary to HTML Microdata. Only use WordPress themes and plugins that support schema to get the SEO benefits.
Compatibility
Be sure that any plugin you install is compatible with the WordPress theme you are using. If you get a warning during installation, heed it. Conflicts can cause issues with your .htaccess files, sitemaps and robots.txt files. You could also end up duplicating page elements such as titles and headings which is bad for SEO.
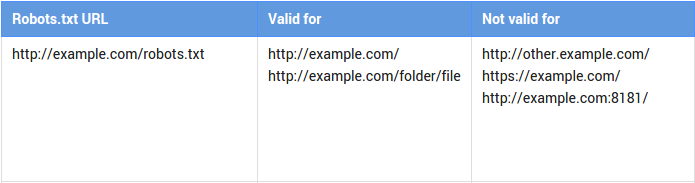
here are pages on a website that you may not want indexed because they aren’t geared towards users. For example, admin, archive and tag pages. The same goes for “thank you” pages that load after the submission of a form. It doesn’t make much sense to index such pages because you wouldn’t send traffic directly to such a page in the first place.
Tag pages and category pages could also be deemed to contain duplicate content by search engines. Using my earlier example, it is possible to have a tag and category page for “smartphones”. To the search engines, this would be duplicate content.
To block pages you don’t want indexed, block them using the Robots.txt file by adding the following lines of code:
If you want to block all search engines, use this code:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /[relative page url]If you only want to block Google, use this code:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /[relative page url]
However, do not overdo it. Abusing this feature will be counterproductive for SEO.
Step 6: WordPress.org vs. WordPress.com
This one is straight forward. Hosting your site on WordPress.com is good enough if its a hobby blog or simple personal site. However, if you are running a business or serious organization, you should consider something more powerful and customizable.
WordPress.com tends to limit what you can do for your site’s SEO. To get the full benefits of WordPress, I recommend moving your site to a self-hosted WordPress.org site.
This way, you can fully customize themes, plugins and widgets for the best SEO.
Also, all the points below refer specifically to self-hosted WordPress websites.
