ReviewCoreASPHosting.NET | Best and cheap ASP.NET core 1.0 hosting. In this tutorial, you will learn how to build and run your first asp.net core docker image.
You will need to install dotnet core and docker on your machine before you begin this tutorial.
If you are running behind a proxy some of the commands might not work, so be sure to check out the Proxy-Section below.
The Dockerfile
If you already have basic knowledge of Docker skip this introduction and go straight to “Choose an image”.
You can run one of the many images that exist ready for usage on hub.docker.com. You can for example
run a command on an instance of Debian a popular Linux Distro with the following command:
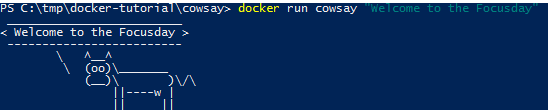
docker run debian echo "Welcome to Docker"
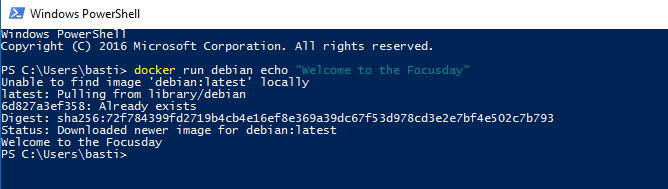
This might take a while the first time, since docker has to pull the image. A second run should start the command in a fraction of a second.
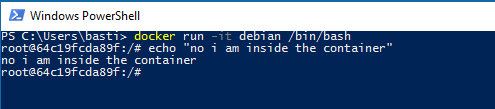
Instead of running a “throw away”-container you can also use an container interactively like so:
docker run -it debian /bin/bash
Check out the docker run reference to find out more: docker run
You can exit the container by typing “exit” and hitting enter.
But you can not only run other peoples images, you can also create your own images. For that you will need to create a Dockerfile. The Dockerfile describes an image and all its dependencies in steps.
We can start with a simple Dockerfile that extends our hello world example.
Create a new folder called cowsay and add a file called Dockerfile. Add the following content to the file:
FROM debian RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y cowsay ENTRYPOINT ["/usr/games/cowsay"]
In this dockerfile we are doing the follwing:
- defining what base image we want to use => debian
- running a command in the image that updates the packagemanager and installs an app called cowsay
- defining what app to run when the image is run
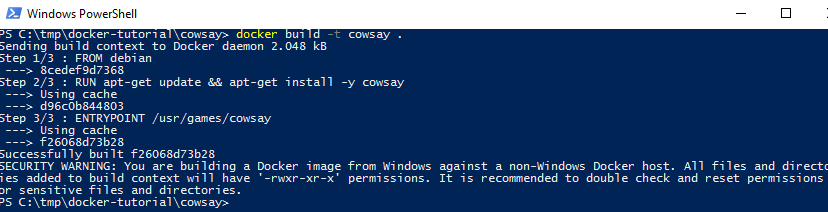
Now let’s build the image with the build command from the created folder:
docker build -t cowsay .
If this hangs and you are running behind a proxy check this out.
Now that we have build our image we can run it:
docker run cowsay "Welcome to Docker"
Choose an image
Go to hub.docker.com and search for aspnetcore
You will find many different choices. If there are no very special reasons i would opt for official images or images uploaded by the involved companies. Two images are interesting:
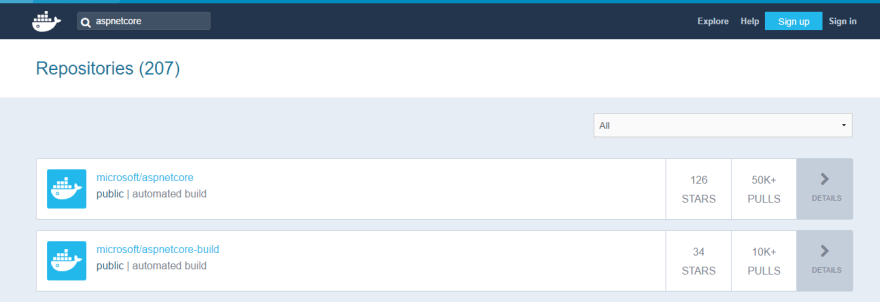
There are two different images provided by microsoft. One of them only contains the runtime and the other contains the SDK as well – see the following descriptions
ASP.NET Core Docker Image
This repository contains images for running published ASP.NET Core applications. These images use the
microsoft/dotnet image as its base.
ASP.NET Core Build Docker Image
This repository contains images that are used to compile/publish ASP.NET Core applications inside the container. This is different to compiling an ASP.NET Core application and then adding the compiled output to an image, which is what you would do when using the microsoft/aspnetcore image. These Dockerfiles use the microsoft/dotnet image as its base.
Create a asp.net core project
create a folder called docker-tutorial and navigate to it, then execute the following command:
dotnet new webapi
First Build
Let’s start easy and compile the app on our computer and then add the output to the runtime image.
Run the following commands in the root of your project:
dotnet restore dotnet publish -o ./publish
You should now have a publish folder, that contains your compiled application.
Now create a new Dockerfile in the root of the application
FROM microsoft/aspnetcore WORKDIR /app COPY ./publish . ENTRYPOINT ["dotnet", "docker-tutorial.dll"]
This Dockerimage will copy the contents of the publish folder in the root of your project into the app folder on the image.
Build the image:
docker build -t docker-tutorial .
You can find out more about the build command here
Test the image:
docker run -p 8181:80 docker-tutorial
Now you can navigate to the hosted application: http://localhost:8181/api/values
You should get a response like this:
["value1","value2"]
Your docker engine might not be reachable through localhost. If so change to the correct url. If you
are using the docker toolbox with docker-machine you can get the ip with the following command:
docker-machine ip default
Compiling within the aspnetcore-build image
It is recommended to compile your project within the docker image, since this will produce a more reliable build pipeline. The build on the development machine will work the same way as the build in the build server.
So let’s create another Dockerfile called Dockerfile.build
FROM microsoft/aspnetcore-build WORKDIR /app COPY *.csproj . RUN dotnet restore COPY . . RUN dotnet publish --output /out/ --configuration Release
The new instruction we use here is COPY. This copies files from our host into the image.
Also note what happens when you rebuild the image. If you don’t change anything nothing will be done. If you change something in the code the publish instruction will be executed but not dotnet restore. Only if you change some dependency will the dotnet restore instruction be executed.
For a more detailed description of this “layered” build process check this out.
Before we build the “build-image” we need to add one more file to avoid that dotnet commands on our host (dotnet restore/build) interfere with the build context. See this for more information. Add a file called .dockerignore with the following content to the root of the project:
bin obj
Now let’s build the image. Note we have to explicitly specify what Dockerfile we want to use:
docker build -f Dockerfile.build -t docker-tutorial-build .
With our image build and the project compiled we now want to get at the compiled app. First we create the container with the create command. This is almost like docker run just that the container is never really started. We can however copy out the compiled app.
docker create --name docker-tutorial-build-container docker-tutorial-build
! delete the earlier created publish folder – we will now copy the containers compiled result into that folder:
docker cp docker-tutorial-build-container:/out ./publish
Great now we can build the runtime image just like before:
docker build -t docker-tutorial .
And of course run it:
docker run -p 8181:80 docker-tutorial
! You probably have to stop the container we started earlier, since that one is already using port 8181. To do so first list the running processes:
docker ps
Copy the container ID, e.g. ba51e5dc4036
and run the following command:
docker rm $(docker stop ba51e5dc4036)
Publishing & Pulling Images
Now that we build the image it would be nice if we could use that on other docker hosts. To do so we can upload our image to a docker registry.
There are many different choices for docker registries: hub.docker.com, AWS ECR, Artifactory…
For simplicity we will be using hub.docker.com which is free for public images.
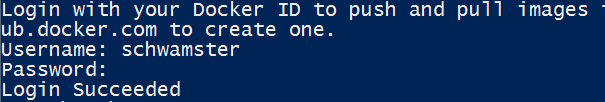
If you havent done so yet, create an account .
You can then logon in powershell:
docker login
To be able to upload (push) our image we have to prefix our image with our username. My username is schwamster so I would have to run the following command:
docker tag docker-tutorial schwamster/docker-tutorial
Now I can push the image
docker push schwamster/docker-tutorial
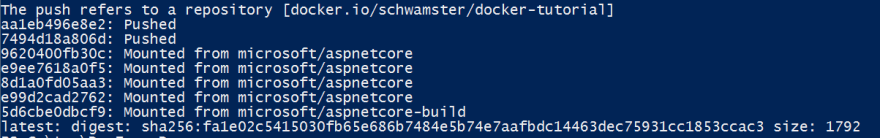
After the image is pushed I can verify that it worked by opening the following url: https://hub.docker.com/r/schwamster/docker-tutorial/
To pull the image run the following command:
Now you can also run my image like this:
docker run -p 8182:80 schwamster/docker-tutorial
My image will now be pulled and run on your machine. Check it out under http://localhost:8182/api/values (Changed port to 8182)
Proxy
If you are forced to go through a proxy you will have to adjust some of the commands we used above.
Proxy and docker run
If you need to have internet access from within your container you will have to add the proxy settings to respective environment variables of the container instance. Those can be different depending on what application you use. In general I would set the following:
- http_proxy
- https_proxy
I noticed that some applications want the variables to be set uppercase -> HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY. Other apps might need dedicated environment variables or even changes in config files.
To add the proxy environment variables add each environment variable with the -e argument
Here is an example:
docker run -it -e https_proxy=http://someproxy:8080 -e http_proxy=http://someproxy:8080 debian /bin/bash
To test this run the following command in your container:
apt-get update
apt-get update should now work and not run into a timeout.
Proxy and docker build
If you need internet access while building the image you need to pass the environment variables with the –build-arg argument just like you do it with run time environment variables. Its just the argument that is called different.
Example:
docker build --build-arg http_proxy=http://someproxy:8080 --build-arg https_proxy=http://someproxy:8080 -t cowsay .